Difference between revisions of "Material:Gold"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Properties) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Properties) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
[[Image:Gold-critq.png|400px]][[Image:Gold-SLD.png|400px]] | [[Image:Gold-critq.png|400px]][[Image:Gold-SLD.png|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Gold-AttLen.png|400px]][[Image:Gold-mu.png|400px]] | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gold Wikipedia: Gold] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gold Wikipedia: Gold] | ||
Revision as of 11:16, 9 June 2014
Gold is a dense, soft metal. In scattering experiments, it is frequently encountered because it is a material of choice for nanoparticles.
Properties
- Density: 19.30 g/cm3
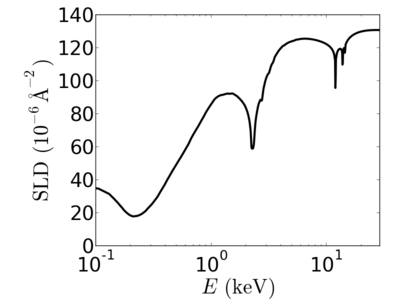
- Neutron SLD: 4.662×10−6 Å−2
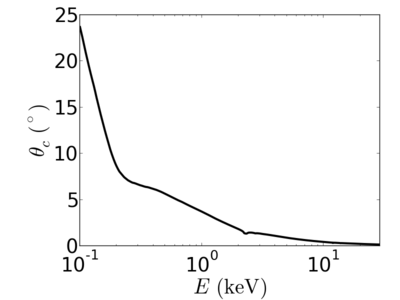
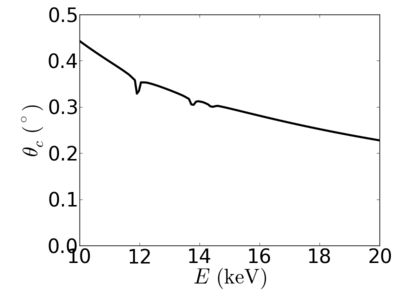
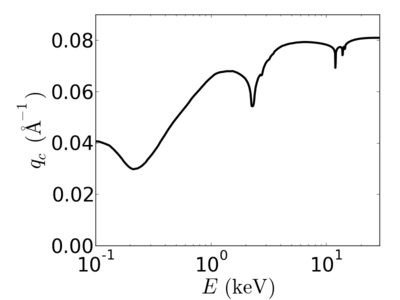
| Material | density (g/cm3) | X-ray energy (keV) | X-ray wavelength (Å) | critical angle (°) | qc (Å−1) | SLD (10−6Å−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 19.32 | 2.0 | 6.20 | 1.830 | 0.0647 | 83.44 |
| 4.0 | 3.10 | 1.097 | 0.0776 | 119.89 | ||
| 8.0 | 1.55 | 0.560 | 0.0792 | 124.86 | ||
| 12.0 | 1.03 | 0.348 | 0.0738 | 108.29 | ||
| 16.0 | 0.77 | 0.282 | 0.0797 | 126.51 | ||
| 24.0 | 0.52 | 0.191 | 0.0811 | 130.80 |