Circular orientation distribution function
In assessing the orientation of aligned materials, one can use the orientation order parameter to quantify order. Another possibility is to fit scattering data using an equation that has 'circular wrapping' (i.e. periodic along ).
Contents
function
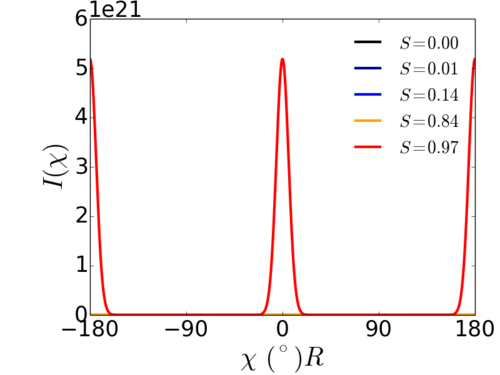
Ruland et al. present such an equation:
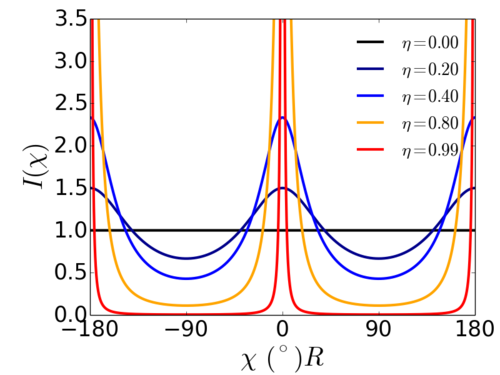
Where is the angle along the arc of the scattering ring/feature. The single fit parameter () is convenient in that it behaves in a similar way to an order parameter: a value close to 1.0 indicates strong alignment, while progressively smaller values indicate lesser alignment. For a random sample, the scattering is isotropic and .
Normalized
The function normalized so that the maximum is always at 1 would be:
References
- Ruland, W.; Tompa, H., The Effect of Preferred Orientation on the Intensity Distribution of (Hk) Interferences. Acta Crystallographica Section A 1968, 24, 93-99. 10.1107/S0567739468000112
- Ruland, W.; Smarsly, B., Saxs of Self-Assembled Oriented Lamellar Nanocomposite Films: An Advanced Method of Evaluation. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2004, 37, 575-584. doi: 10.1107/S0021889804011288
- Kevin G. Yager, Christopher Forrey, Gurpreet Singh, Sushil K. Satija, Kirt A. Page, Derek L. Patton, Jack F. Douglas, Ronald L. Jones and Alamgir Karim Thermally-induced transition of lamellae orientation in block-copolymer films on ‘neutral’ nanoparticle-coated substrates Soft Matter 2015 doi: 10.1039/C5SM00896D
- De France, K.J.; Yager, K.G.; Hoare, T.; Cranston, E.D. "Cooperative Ordering and Kinetics of Cellulose Nanocrystal Alignment in a Magnetic Field" Langmuir 2016, 32, 7564–7571. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01827
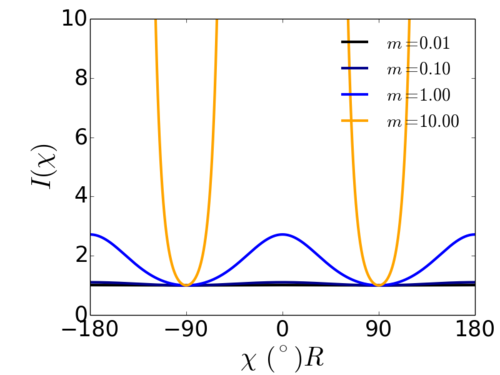
Maier-Saupe distribution parameter
Where is a parameter that can be related to the order parameter ; specifically is for an isotropic distribution (), while is for a well-aligned system ().
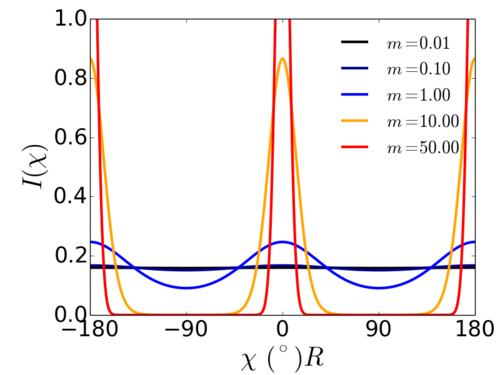
The parameter c can be used to normalize:







![{\displaystyle I(\chi )={\frac {1}{c}}\exp \left[m\cos ^{2}\chi \right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/49bde8b233a0c9f4c7f1b73ce1fd95128a73bb00)