Difference between revisions of "Atomic scattering factors"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (Created page with "The '''atomic scattering factors''' are measures of the scattering power of individual atoms. Each element has a different atomic scattering factor (which in turn varies w...") |
(→Energy dependence) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The atomic scattering factors vary with x-ray wavelength. In particular, a given element will have resonant edges at certain energies, where the absorption increases markedly. The dispersive component ''f''<sub>1</sub> will also vary rapidly in the vicinity of an absorption edge (c.f. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kramers%E2%80%93Kronig_relations Kramers-Kronig relations]). | The atomic scattering factors vary with x-ray wavelength. In particular, a given element will have resonant edges at certain energies, where the absorption increases markedly. The dispersive component ''f''<sub>1</sub> will also vary rapidly in the vicinity of an absorption edge (c.f. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kramers%E2%80%93Kronig_relations Kramers-Kronig relations]). | ||
| − | + | ===Examples=== | |
| + | |||
| + | ====[[Material:Silicon|silicon]]==== | ||
[[Image:Silicon-atomic scatt factor.png|400px|[[Atomic scattering factors]] (''f''<sub>1</sub> and ''f''<sub>2</sub>).]] | [[Image:Silicon-atomic scatt factor.png|400px|[[Atomic scattering factors]] (''f''<sub>1</sub> and ''f''<sub>2</sub>).]] | ||
| + | |||
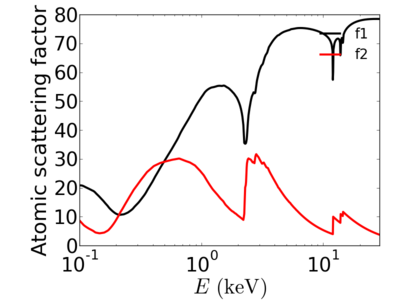
| + | ====[[Material:Gold|gold]]==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Gold-atomic scatt factor.png|400px|[[Atomic scattering factors]] (''f''<sub>1</sub> and ''f''<sub>2</sub>).]] | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/asf.html Periodic table of atomic scattering factors]: Useful tool for looking up the values for any element. | * [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/asf.html Periodic table of atomic scattering factors]: Useful tool for looking up the values for any element. | ||
* [http://reference.iucr.org/dictionary/Atomic_scattering_factor Online Dictionary of Crystallography: Atomic scattering factor] | * [http://reference.iucr.org/dictionary/Atomic_scattering_factor Online Dictionary of Crystallography: Atomic scattering factor] | ||
Revision as of 11:48, 5 June 2014
The atomic scattering factors are measures of the scattering power of individual atoms. Each element has a different atomic scattering factor (which in turn varies with x-ray energy), which represents how strongly x-rays interact with those atoms. Because x-ray interactions occur with an atom's electron cloud, the scattering factors increase with number of electrons, and thus with atomic number (Z).
The scattering factor has two components: f1 and f2, which describe the dispersive and absorptive components. In other words, f2 describes how strongly the material absorbs the radiation, while f1 describes the non-absorptive interaction (which leads to refraction).
Energy dependence
The atomic scattering factors vary with x-ray wavelength. In particular, a given element will have resonant edges at certain energies, where the absorption increases markedly. The dispersive component f1 will also vary rapidly in the vicinity of an absorption edge (c.f. Kramers-Kronig relations).
Examples
silicon
gold
See Also
- Periodic table of atomic scattering factors: Useful tool for looking up the values for any element.
- Online Dictionary of Crystallography: Atomic scattering factor