Difference between revisions of "Absorption length"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Related forms) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→See Also) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
where ''ρ'' is density, ''N<sub>a</sub>'' is the Avogadro constant, and ''m<sub>a</sub>'' is the atomic molar mass. Note that the '''mass attenuation coefficient''' is simply <math>\mu/\rho</math>. | where ''ρ'' is density, ''N<sub>a</sub>'' is the Avogadro constant, and ''m<sub>a</sub>'' is the atomic molar mass. Note that the '''mass attenuation coefficient''' is simply <math>\mu/\rho</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Elemental dependence== | ||
| + | |||
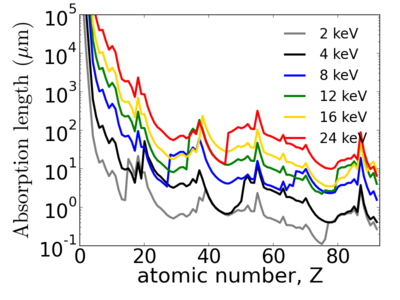
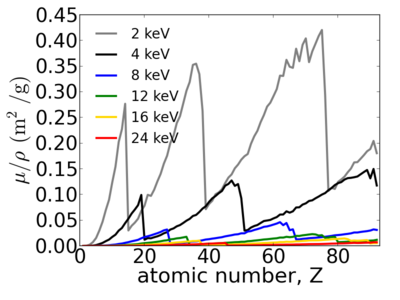
| + | [[Image:Elements-abs.png|400px]][[Image:Elements-mu.png|400px]] | ||
==Energy dependence== | ==Energy dependence== | ||
| + | Notice that the absorption undergoes sharp increases when passing through an absorption edge. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 42: | ||
[[Image:Gold-AttLen.png|400px]][[Image:Gold-mu.png|400px]] | [[Image:Gold-AttLen.png|400px]][[Image:Gold-mu.png|400px]] | ||
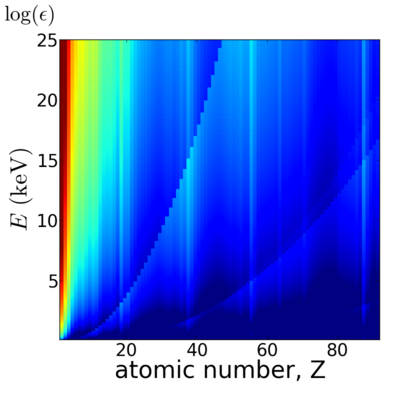
| + | ==Elemental/Energy dependence== | ||
| + | [[Image:Elements2D-abs.png|400px]][[Image:Elements2D-mu.png|400px]] | ||
==Related forms== | ==Related forms== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 115: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | See also '''[[Atomic_scattering_factors#Related_forms|scattering factors]]''' for a comparison of the quantities related to ''f''<sub>1</sub>. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| + | * [[Resonant scattering]] | ||
| + | ** [[RSoXS]] | ||
| + | ** [[Resonant reflectivity]] | ||
* [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/atten2.html LBL X-Ray Attenuation Length calculator] | * [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/atten2.html LBL X-Ray Attenuation Length calculator] | ||
* [http://11bm.xray.aps.anl.gov/absorb/absorb.php APS absorption calculator] | * [http://11bm.xray.aps.anl.gov/absorb/absorb.php APS absorption calculator] | ||
| + | * [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/filter2.html CXRO transmission calculator] | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_attenuation_coefficient Wikipedia: Mass attenuation coefficient] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_attenuation_coefficient Wikipedia: Mass attenuation coefficient] | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absorption_cross_section Wikipedia: Absorption cross sectio] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absorption_cross_section Wikipedia: Absorption cross sectio] | ||
* [http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xraycoef/ NIST tables of x-ray mass attenuation coefficient] | * [http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xraycoef/ NIST tables of x-ray mass attenuation coefficient] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 29 July 2015
The absorption length or attenuation length in x-ray scattering is the distance over which the x-ray beam is absorbed. By convention, the absorption length ϵ is defined as the distance into a material where the beam flux has dropped to 1/e of its incident flux.
Contents
Absorption
The absorption follows a simple Beer-Lambert law:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{I(x)}{I_0} = e^{ - x / \epsilon } }
The attenuation coefficient (or absorption coefficient) is simply the inverse of the absorption length;
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{I(x)}{I_0} = e^{ - \mu x } }
Calculating
The absorption length arises from the imaginary part of the atomic scattering factor, f2. It is closely related to the absorption cross-section, and the mass absorption coefficient. Specifically, the atomic photoabsorption cross-section can be computed via:
Where λ is the x-ray wavelength, and re is the classical electron radius. The attenuation coefficient is given by:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{alignat}{2} \mu & = \frac{\rho N_a}{m_a} \sigma \\ & = \frac{\rho N_a}{m_a} 2 r_e \lambda f_2 \end{alignat} }
where ρ is density, Na is the Avogadro constant, and ma is the atomic molar mass. Note that the mass attenuation coefficient is simply Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu/\rho} .
Elemental dependence
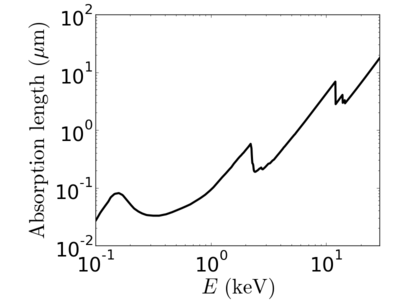
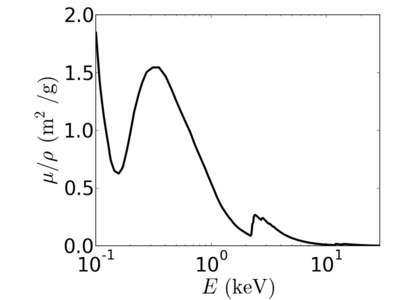
Energy dependence
Notice that the absorption undergoes sharp increases when passing through an absorption edge.
Examples
silicon
gold
Elemental/Energy dependence
Related forms
As can be seen, there are many related quantities which express the material's absorption:
- Absorption length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon} , the distance over which the intensity falls to 1/e.
- Attenuation coefficient Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu} , the characteristic inverse-distance for attenuation.
- Mass attenuation coefficient Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu/\rho} , the density-scaled attenuation.
- Absorptive atomic scattering factor , the intrinsic dissipative interaction of the material.
- Atomic photoabsorption cross-section Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma} , the cross-section ('effective size') of the atom's x-ray absorption (capture) efficiency.
- Imaginary refractive index Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} , the resonant component of the refractive index.
- Imaginary Scattering Length Density Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} , the absorptive component of the scattering contrast.
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon = \frac{1}{\mu}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon = \frac{\rho}{\mu/\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon = \frac{M_a}{\rho N_a 2 r_e \lambda f_2 }} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon = \frac{M_a}{\rho N_a \sigma}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon = \frac{ \lambda }{4 \pi \beta}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon = \frac{1}{2 \lambda \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} } |
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu = \frac{1}{\epsilon}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu = \frac{\mu/\rho}{\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu = \frac{\rho N_a}{M_a} 2 r_e \lambda f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu = \frac{\rho N_a}{M_a} \sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu = \frac{4 \pi }{ \lambda } \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu = 2 \lambda\mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho} = \frac{1}{\rho\epsilon}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho} = \mu/\rho} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho} = \frac{N_a}{M_a} 2 r_e \lambda f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho} = \frac{N_a}{M_a} \sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho} = \frac{4 \pi}{ \rho \lambda } \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\mu}{\rho} = \frac{2 \lambda}{\rho } \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2 = \frac{M_a }{\rho N_a 2 r_e \lambda \epsilon} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2 = \frac{M_a }{\rho N_a 2 r_e \lambda} \mu } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2 = \frac{M_a }{ N_a 2 r_e \lambda} \frac{\mu}{\rho} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2 = \frac{\sigma}{2 r_e \lambda}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2 = \frac{2 \pi M_a}{ \rho N_a r_e \lambda^2 } \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_2 = \frac{M_a}{\rho N_a r_e } \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = \frac{M_a}{\rho N_a \epsilon} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = \frac{M_a}{\rho N_a} \mu} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = \frac{M_a}{N_a} \frac{\mu}{\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = 2 r_e \lambda f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = \frac{4 \pi M_a}{ \rho N_a \lambda } \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = \frac{2 \lambda M_a}{\rho N_a}\mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \lambda }{4 \pi \epsilon}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \lambda }{4 \pi } \mu} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \rho \lambda }{4 \pi } \frac{\mu}{\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \rho N_a r_e \lambda^2 }{2 \pi M_a} f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \rho N_a \lambda }{4 \pi M_a} \sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{\lambda^2}{2 \pi} \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{1 }{2 \lambda \epsilon} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\mu}{2 \lambda} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\rho }{2 \lambda} \frac{\mu}{\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\rho N_a r_e }{M_a} f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\rho N_a}{2 \lambda M_a}\sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{2 \pi }{\lambda^2} \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
See also scattering factors for a comparison of the quantities related to f1.