Difference between revisions of "Absorption length"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Elemental/Energy dependence) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→See Also) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | See also '''[[Atomic_scattering_factors#Related_forms|scattering factors]]''' for a comparison of the quantities related to ''f''<sub>1</sub>. | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| + | * [[Resonant scattering]] | ||
| + | ** [[RSoXS]] | ||
| + | ** [[Resonant reflectivity]] | ||
* [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/atten2.html LBL X-Ray Attenuation Length calculator] | * [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/atten2.html LBL X-Ray Attenuation Length calculator] | ||
* [http://11bm.xray.aps.anl.gov/absorb/absorb.php APS absorption calculator] | * [http://11bm.xray.aps.anl.gov/absorb/absorb.php APS absorption calculator] | ||
| + | * [http://henke.lbl.gov/optical_constants/filter2.html CXRO transmission calculator] | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_attenuation_coefficient Wikipedia: Mass attenuation coefficient] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_attenuation_coefficient Wikipedia: Mass attenuation coefficient] | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absorption_cross_section Wikipedia: Absorption cross sectio] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Absorption_cross_section Wikipedia: Absorption cross sectio] | ||
* [http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xraycoef/ NIST tables of x-ray mass attenuation coefficient] | * [http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xraycoef/ NIST tables of x-ray mass attenuation coefficient] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 29 July 2015
The absorption length or attenuation length in x-ray scattering is the distance over which the x-ray beam is absorbed. By convention, the absorption length ϵ is defined as the distance into a material where the beam flux has dropped to 1/e of its incident flux.
Contents
Absorption
The absorption follows a simple Beer-Lambert law:
The attenuation coefficient (or absorption coefficient) is simply the inverse of the absorption length;
Calculating
The absorption length arises from the imaginary part of the atomic scattering factor, f2. It is closely related to the absorption cross-section, and the mass absorption coefficient. Specifically, the atomic photoabsorption cross-section can be computed via:
Where λ is the x-ray wavelength, and re is the classical electron radius. The attenuation coefficient is given by:
where ρ is density, Na is the Avogadro constant, and ma is the atomic molar mass. Note that the mass attenuation coefficient is simply .
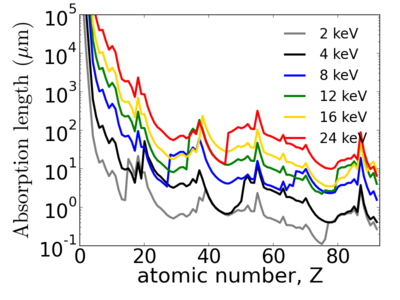
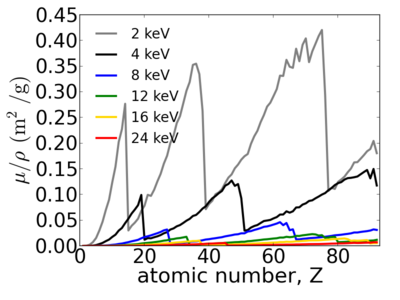
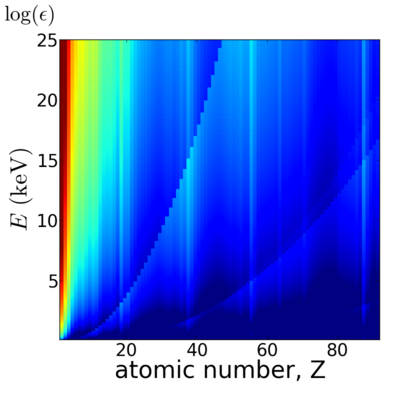
Elemental dependence
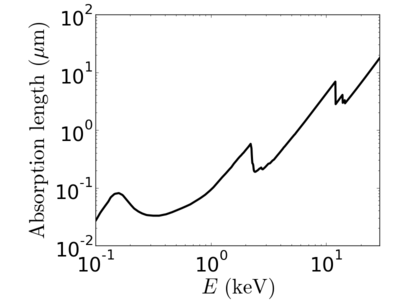
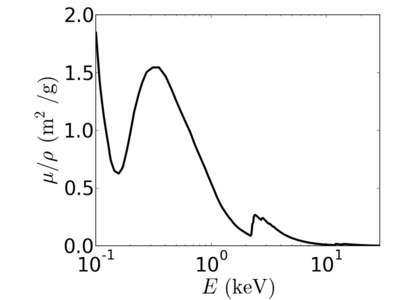
Energy dependence
Notice that the absorption undergoes sharp increases when passing through an absorption edge.
Examples
silicon
gold
Elemental/Energy dependence
Related forms
As can be seen, there are many related quantities which express the material's absorption:
- Absorption length , the distance over which the intensity falls to 1/e.
- Attenuation coefficient , the characteristic inverse-distance for attenuation.
- Mass attenuation coefficient , the density-scaled attenuation.
- Absorptive atomic scattering factor , the intrinsic dissipative interaction of the material.
- Atomic photoabsorption cross-section , the cross-section ('effective size') of the atom's x-ray absorption (capture) efficiency.
- Imaginary refractive index , the resonant component of the refractive index.
- Imaginary Scattering Length Density , the absorptive component of the scattering contrast.
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \rho N_a r_e \lambda^2 }{2 \pi M_a} f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{ \rho N_a \lambda }{4 \pi M_a} \sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{\lambda^2}{2 \pi} \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} | |||
| Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{1 }{2 \lambda \epsilon} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\mu}{2 \lambda} } | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\rho }{2 \lambda} \frac{\mu}{\rho}} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\rho N_a r_e }{M_a} f_2} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{\rho N_a}{2 \lambda M_a}\sigma} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD}) = \frac{2 \pi }{\lambda^2} \beta} | Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathrm{Im}(\mathrm{SLD})} |
See also scattering factors for a comparison of the quantities related to f1.