Difference between revisions of "Increasing AI Intelligence"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→CoT reasoning model) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→CoT reasoning model) |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
* 2025-01: [https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-k1.5/blob/main/Kimi_k1.5.pdf Kimi k1.5: Scaling Reinforcement Learning with LLMs] | * 2025-01: [https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-k1.5/blob/main/Kimi_k1.5.pdf Kimi k1.5: Scaling Reinforcement Learning with LLMs] | ||
* 2025-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11223 Reasoning Language Models: A Blueprint] | * 2025-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11223 Reasoning Language Models: A Blueprint] | ||
| + | * 2025-01: [https://huggingface.co/blog/open-r1 Open-R1: a fully open reproduction of DeepSeek-R1] | ||
===Scaling=== | ===Scaling=== | ||
Revision as of 12:07, 29 January 2025
Contents
- 1 Reviews
- 2 Prompt Engineering
- 3 Fine Tuning
- 4 Proactive Search
- 5 Inference Time Compute
- 5.1 Methods
- 5.1.1 In context learning (ICL), search, and other inference-time methods
- 5.1.2 Inference-time Sampling
- 5.1.3 Inference-time Gradient
- 5.1.4 Self-prompting
- 5.1.5 Retrieval or Memory
- 5.1.6 In-context thought
- 5.1.7 Naive multi-LLM (verification, majority voting, best-of-N, etc.)
- 5.1.8 Multi-LLM (multiple comparisons, branching, etc.)
- 5.1.9 Iteration (e.g. neural-like layered blocks)
- 5.1.10 Iterative reasoning via graphs
- 5.1.11 Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)
- 5.1.12 Other Search
- 5.1.13 Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
- 5.2 Analysis
- 5.3 Pragmatics
- 5.1 Methods
- 6 Interact with Environment
- 7 Memory
- 8 Tool Use
- 9 Multi-agent Effort (and Emergent Intelligence)
- 10 ML-like Optimization of LLM Setup
- 11 Limitations/Requirements
- 12 See Also
Reviews
- 2024-12: A Survey of Mathematical Reasoning in the Era of Multimodal Large Language Model: Benchmark, Method & Challenges
- 2025-01: Test-time Computing: from System-1 Thinking to System-2 Thinking (github list of papers)
- 2025-01: Reasoning Language Models: A Blueprint
- Links to papers: Awesome LLM Strawberry (OpenAI o1)
Prompt Engineering
Fine Tuning
- 2024-12: Inference-Aware Fine-Tuning for Best-of-N Sampling in Large Language Models
- 2025-01: AgentRefine: Enhancing Agent Generalization through Refinement Tuning
- 2025-01: Multiagent Finetuning: Self Improvement with Diverse Reasoning Chains (preprint, code)
Proactive Search
Compute expended after training, but before inference.
Training Data (Data Refinement, Synthetic Data)
- C.f. image datasets:
- 2024-09: Programming Every Example: Lifting Pre-training Data Quality like Experts at Scale
- 2024-10: Data Cleaning Using Large Language Models
- Updating list of links: Synthetic Data of LLMs, by LLMs, for LLMs
Generate consistent plans/thoughts
- 2024-08: Mutual Reasoning Makes Smaller LLMs Stronger Problem-Solvers (code)
- (Microsoft) rStar is a self-play mutual reasoning approach. A small model adds to MCTS using some defined reasoning heuristics. Mutually consistent trajectories can be emphasized.
- 2024-09: Self-Harmonized Chain of Thought
- Produce refined chain-of-thought style solutions/prompts for diverse problems. Given a large set of problems/questions, first aggregated semantically, then apply zero-shot chain-of-thought to each problem. Then cross-pollinate between proposed solutions to similar problems, looking for refined and generalize solutions.
- 2024-11: LLMs Do Not Think Step-by-step In Implicit Reasoning
- They argue that models trained to reproduce CoT outputs do not, internally, perform stepwise reasoning (with intermediate representations); this suggests that explicit CoT could be superior to implicit CoT.
Sampling
- 2024-11: Language Models are Hidden Reasoners: Unlocking Latent Reasoning Capabilities via Self-Rewarding (code)
Automated prompt generation
Distill inference-time-compute into model
- 2023-10: Reflection-Tuning: Data Recycling Improves LLM Instruction-Tuning (U. Maryland, Adobe)
- 2023-11: Implicit Chain of Thought Reasoning via Knowledge Distillation (Harvard, Microsoft, Hopkins)
- 2024-02: Grandmaster-Level Chess Without Search (Google DeepMind)
- 2024-07: Fine-Tuning with Divergent Chains of Thought Boosts Reasoning Through Self-Correction in Language Models
- 2024-07: Distilling System 2 into System 1
- 2024-07: BOND: Aligning LLMs with Best-of-N Distillation
- 2024-09: Training Language Models to Self-Correct via Reinforcement Learning (Google DeepMind)
- 2024-10: Thinking LLMs: General Instruction Following with Thought Generation
- 2024-10: Dualformer: Controllable Fast and Slow Thinking by Learning with Randomized Reasoning Traces
- 2024-12: Training Large Language Models to Reason in a Continuous Latent Space
CoT reasoning model
See also: AI tools > LLM > Open-weights LLM > Reasoning
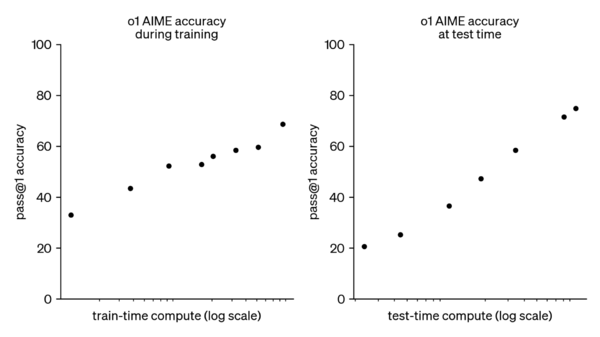
- 2024-09: OpenAI o1
- 2024-10: O1 Replication Journey: A Strategic Progress Report – Part 1 (code): Attempt by Walnut Plan to reproduce o1-like in-context reasoning
- 2024-11: DeepSeek-R1-Lite-Preview reasoning model
- 2024-11: Marco-o1: Towards Open Reasoning Models for Open-Ended Solutions
- 2024-11: O1 Replication Journey -- Part 2: Surpassing O1-preview through Simple Distillation, Big Progress or Bitter Lesson?
- 2024-12: o1-Coder: an o1 Replication for Coding (code)
- 2024-12: Mulberry: Empowering MLLM with o1-like Reasoning and Reflection via Collective Monte Carlo Tree Search
- 2024-12: Scaling of Search and Learning: A Roadmap to Reproduce o1 from Reinforcement Learning Perspective
- 2025-01: Virgo: A Preliminary Exploration on Reproducing o1-like MLLM
- 2025-01: O1 Replication Journey -- Part 3: Inference-time Scaling for Medical Reasoning
- 2025-01: DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning
- 2025-01: Kimi k1.5: Scaling Reinforcement Learning with LLMs
- 2025-01: Reasoning Language Models: A Blueprint
- 2025-01: Open-R1: a fully open reproduction of DeepSeek-R1
Scaling
- 2024-08: Smaller, Weaker, Yet Better: Training LLM Reasoners via Compute-Optimal Sampling (Google DeepMind)
- 2024-11: Scaling Laws for Pre-training Agents and World Models
Inference Time Compute
Methods
- 2024-03: Quiet-STaR: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Think Before Speaking
- 2024-11: Reverse Thinking Makes LLMs Stronger Reasoners
- 2024-12: Training Large Language Models to Reason in a Continuous Latent Space (Chain of Continuous Thought, COCONUT)
Review
- 2024-06: From Decoding to Meta-Generation: Inference-time Algorithms for Large Language Models
- 2025-01: Test-time Computing: from System-1 Thinking to System-2 Thinking (github list of papers)
In context learning (ICL), search, and other inference-time methods
- 2023-03: Reflexion: Language Agents with Verbal Reinforcement Learning
- 2023-05: VOYAGER: An Open-Ended Embodied Agent with Large Language Models
- 2024-04: Many-Shot In-Context Learning
- 2024-08: Automated Design of Agentic Systems
- 2024-09: Planning In Natural Language Improves LLM Search For Code Generation
Inference-time Sampling
- 2024-10: entropix: Entropy Based Sampling and Parallel CoT Decoding
- 2024-10: TreeBoN: Enhancing Inference-Time Alignment with Speculative Tree-Search and Best-of-N Sampling
- 2024-11: Turning Up the Heat: Min-p Sampling for Creative and Coherent LLM Outputs
- 2024-12: Guidance is All You Need: Temperature-Guided Reasoning in Large Language Models
Inference-time Gradient
Self-prompting
- 2023-05: Reprompting: Automated Chain-of-Thought Prompt Inference Through Gibbs Sampling
- 2023-11: Rephrase and Respond: Let Large Language Models Ask Better Questions for Themselves
Retrieval or Memory
In-context thought
- 2022-01: Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models (Google Brain)
- 2023-05: Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models (Google DeepMind)
- 2024-05: Faithful Logical Reasoning via Symbolic Chain-of-Thought
- 2024-06: A Tree-of-Thoughts to Broaden Multi-step Reasoning across Languages
- 2024-09: To CoT or not to CoT? Chain-of-thought helps mainly on math and symbolic reasoning
- 2024-09: Iteration of Thought: Leveraging Inner Dialogue for Autonomous Large Language Model Reasoning (Agnostiq, Toronto)
- 2024-09: Logic-of-Thought: Injecting Logic into Contexts for Full Reasoning in Large Language Models
- 2024-10: A Theoretical Understanding of Chain-of-Thought: Coherent Reasoning and Error-Aware Demonstration (failed reasoning traces can improve CoT)
- 2024-10: Tree of Problems: Improving structured problem solving with compositionality
- 2023-01/2024-10: A Survey on In-context Learning
- 2025-01: Towards System 2 Reasoning in LLMs: Learning How to Think With Meta Chain-of-Thought
Naive multi-LLM (verification, majority voting, best-of-N, etc.)
- 2023-06: LLM-Blender: Ensembling Large Language Models with Pairwise Ranking and Generative Fusion (code)
- 2023-12: Dynamic Voting for Efficient Reasoning in Large Language Models
- 2024-04: Regularized Best-of-N Sampling to Mitigate Reward Hacking for Language Model Alignment
- 2024-08: Dynamic Self-Consistency: Leveraging Reasoning Paths for Efficient LLM Sampling
- 2024-11: Multi-expert Prompting Improves Reliability, Safety, and Usefulness of Large Language Models
- 2024-12: llm-consortium: Multiple LLMs collaboratively solve problems through structured dialogue, evaluation and arbitration
Multi-LLM (multiple comparisons, branching, etc.)
- 2024-10: Thinking LLMs: General Instruction Following with Thought Generation
- 2024-11: Mixtures of In-Context Learners: Multiple "experts", each with a different set of in-context examples; combine outputs at the level of next-token-prediction
- 2024-11: LLaVA-o1: Let Vision Language Models Reason Step-by-Step (code)
Iteration (e.g. neural-like layered blocks)
Iterative reasoning via graphs
- 2023-08: Graph of Thoughts: Solving Elaborate Problems with Large Language Models
- 2023-10: Amortizing intractable inference in large language models (code)
- 2024-09: On the Diagram of Thought: Iterative reasoning as a directed acyclic graph (DAG)
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)
- 2024-05: AlphaMath Almost Zero: process Supervision without process
- 2024-06: ReST-MCTS*: LLM Self-Training via Process Reward Guided Tree Search
- 2024-06: Improve Mathematical Reasoning in Language Models by Automated Process Supervision
- 2024-06: Accessing GPT-4 level Mathematical Olympiad Solutions via Monte Carlo Tree Self-refine with LLaMa-3 8B
- 2024-07: Tree Search for Language Model Agents
- 2024-10: Interpretable Contrastive Monte Carlo Tree Search Reasoning
- 2024-12: Mulberry: Empowering MLLM with o1-like Reasoning and Reflection via Collective Monte Carlo Tree Search
Other Search
Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
- 2017-05: Program Induction by Rationale Generation : Learning to Solve and Explain Algebraic Word Problems
- 2021-11: Training Verifiers to Solve Math Word Problems
- 2024-02: Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Without Prompting
Analysis
Scaling
- 2021-04: Scaling Scaling Laws with Board Games
- 2024-03: Are More LLM Calls All You Need? Towards Scaling Laws of Compound Inference Systems
- 2024-04: The Larger the Better? Improved LLM Code-Generation via Budget Reallocation
- 2024-07: Large Language Monkeys: Scaling Inference Compute with Repeated Sampling
- 2024-08: An Empirical Analysis of Compute-Optimal Inference for Problem-Solving with Language Models
- 2024-08: Scaling LLM Test-Time Compute Optimally can be More Effective than Scaling Model Parameters
- 2024-10: (comparing fine-tuning to in-context learning) Is In-Context Learning Sufficient for Instruction Following in LLMs?
- 2024-11: Inference Scaling FLaws: The Limits of LLM Resampling with Imperfect Verifiers
Theory
Expending compute works
- 2024-06-10: Blog post (opinion): AI Search: The Bitter-er Lesson
- 2024-07-17: Blog post (test): Getting 50% (SoTA) on ARC-AGI with GPT-4o
- 2024-09-12: OpenAI o1: Learning to Reason with LLMs
- 2024-09-16: Scaling: The State of Play in AI
Pitfalls
Pragmatics
Code for Inference-time Compute
- optillm: Inference proxy which implements state-of-the-art techniques to improve accuracy and performance of LLMs (improve reasoning over coding, logical and mathematical queries)
Interact with Environment
- 2025-01: Learn-by-interact: A Data-Centric Framework for Self-Adaptive Agents in Realistic Environments
Memory
Tool Use
- 2024-11: DynaSaur: Large Language Agents Beyond Predefined Actions: writes functions/code to increase capabilities
Integrated
- 2018-08: Neural Arithmetic Logic Units
- 2023-01: Tracr: Compiled Transformers as a Laboratory for Interpretability (code)
- 2024-05: Augmenting Language Models with Composable Differentiable Libraries (pdf)
- 2024-07: Algorithmic Language Models with Neurally Compiled Libraries
- 2024-10: ALTA: Compiler-Based Analysis of Transformers
Multi-agent Effort (and Emergent Intelligence)
- 2024-10: Model Swarms: Collaborative Search to Adapt LLM Experts via Swarm Intelligence
- 2024-10: Agent-as-a-Judge: Evaluate Agents with Agents
- 2024-10: Two are better than one: Context window extension with multi-grained self-injection
- 2024-11: Project Sid: Many-agent simulations toward AI civilization
ML-like Optimization of LLM Setup
- 2023-03: DSPy: Compiling Declarative Language Model Calls into Self-Improving Pipelines (code: Programming—not prompting—Foundation Models)
- 2024-05: Automatic Prompt Optimization with "Gradient Descent" and Beam Search
- 2024-06: TextGrad: Automatic "Differentiation" via Text (gradient backpropagation through text)
- 2024-06: Symbolic Learning Enables Self-Evolving Agents (optimize LLM frameworks)
Limitations/Requirements
- Fluid intelligence (c.f. ARC AGI)
- 2024-06: Open-Endedness is Essential for Artificial Superhuman Intelligence