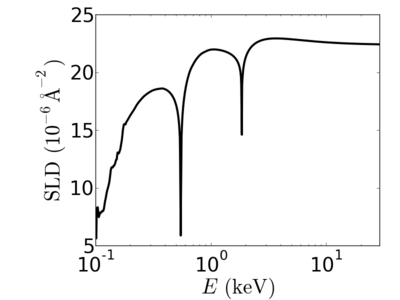
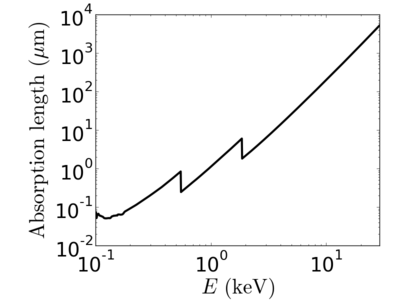
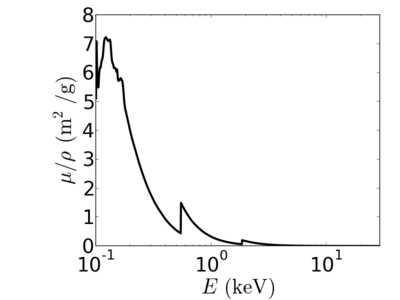
Material:Silicon dioxide
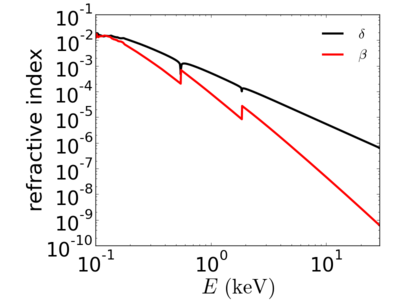
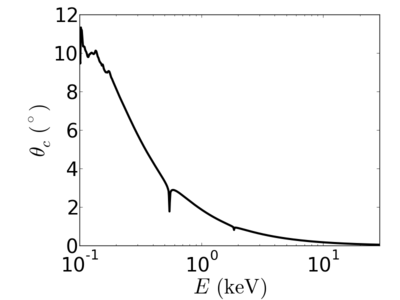
Silicon dioxide (SiO2), also known as silica, spontaneously forms on the surface of a silicon wafer exposed to air. This 'native oxide' must be included in calculations of (for example) the x-ray reflectivity curve for a Si surface. In terms of x-ray properties, SiO2 can be used to approximate a variety of related materials (fused quartz, glass, etc.).
Properties
- Density: 2.648 g/cm3
- Neutron SLD: 4.183×10−6 Å−2
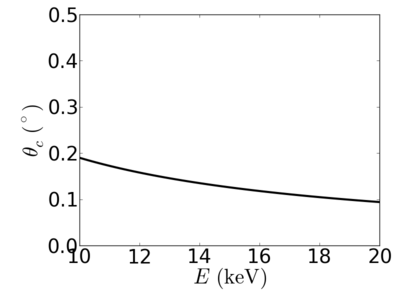
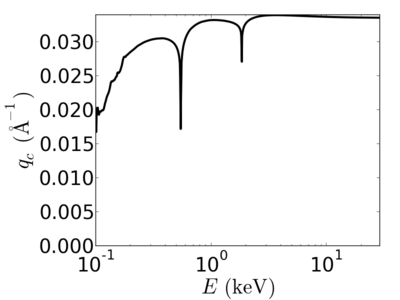
| Material | density (g/cm3) | X-ray energy (keV) | X-ray wavelength (Å) | critical angle (°) | qc (Å−1) | SLD (10−6Å−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 2.648 | 2.0 | 6.20 | 0.927 | 0.0328 | 21.42 |
| 4.0 | 3.10 | 0.480 | 0.0340 | 22.96 | ||
| 8.0 | 1.55 | 0.239 | 0.0338 | 22.71 | ||
| 12.0 | 1.03 | 0.159 | 0.0337 | 22.58 | ||
| 13.5 | 0.92 | 0.141 | 0.0337 | 22.56 | ||
| 16.0 | 0.77 | 0.119 | 0.0337 | 22.53 | ||
| 24.0 | 0.52 | 0.079 | 0.0336 | 22.48 |