Difference between revisions of "GIWAXS"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Grazing-Incidence Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering''' ('''GIWAXS''') is a structural measurement technique wherein wide-angle [[scattering]] is collected; i.e. large values of the [[momentum transfer]]. Because of the [[Fourier transform|inverse nature]] of [[reciprocal-space]], these large values of ''q'' [[Q value|correspond]] to small distances; WAXS generically probes molecular length-scales. | + | '''Grazing-Incidence Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering''' ('''GIWAXS''') is a structural measurement technique wherein wide-angle [[scattering]] is collected; i.e. large values of the [[momentum transfer]]. Because of the [[Fourier transform|inverse nature]] of [[reciprocal-space]], these large values of ''q'' [[Q value|correspond]] to small distances; [[WAXS]] generically probes molecular length-scales. |
| − | There is no unambiguous delineation between WAXS and SAXS; generally speaking, WAXS corresponds to angles from approximately 1° to 45°, or ''q''-values from 0.1 Å<sup>−1</sup> to 5 Å<sup>−1</sup> (6 nm to Angstroms). | + | There is no unambiguous delineation between WAXS and SAXS; generally speaking, WAXS corresponds to angles from approximately 1° to 45°, or ''q''-values from 0.1 Å<sup>−1</sup> to 5 Å<sup>−1</sup> ([[realspace]] distances from 6 nm to Angstroms). |
==Example Data== | ==Example Data== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* A thin film of rubrene: | * A thin film of rubrene: | ||
[[Image:Rubrene GIWAXS example.png|300px]] | [[Image:Rubrene GIWAXS example.png|300px]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[GISAXS]] | * [[GISAXS]] | ||
Revision as of 16:12, 14 October 2014
Grazing-Incidence Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering (GIWAXS) is a structural measurement technique wherein wide-angle scattering is collected; i.e. large values of the momentum transfer. Because of the inverse nature of reciprocal-space, these large values of q correspond to small distances; WAXS generically probes molecular length-scales.
There is no unambiguous delineation between WAXS and SAXS; generally speaking, WAXS corresponds to angles from approximately 1° to 45°, or q-values from 0.1 Å−1 to 5 Å−1 (realspace distances from 6 nm to Angstroms).
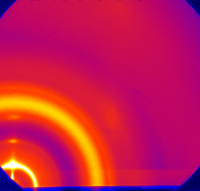
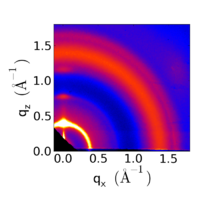
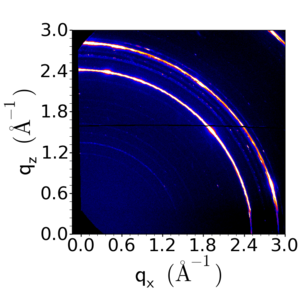
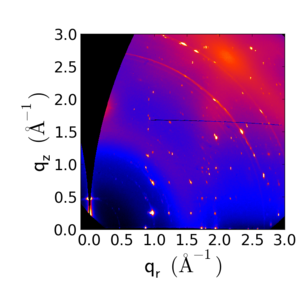
Example Data
- Different representations of data from a P3HT thin film
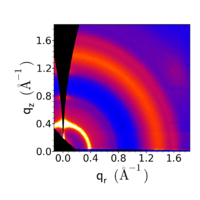 Data converted to q-space, taking into account the Ewald sphere (notice the 'missing wedge' near the qz axis). |
- A Tungsten-Nickel alloy:
- A thin film of rubrene: