Difference between revisions of "Form Factor:Superball"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Mathematical descriptions of superballs) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
====Mathematical descriptions of superballs==== | ====Mathematical descriptions of superballs==== | ||
| − | * N. D. Elkies, A. M. Odlyzko and J. A. Rush "[http://www.springerlink.com/content/l481484244n16157/ On the packing densities of superballs and other bodies]" Inventiones Mathematicae Volume 105, Number 1 (1991), 613-639, [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01232282 | + | * N. D. Elkies, A. M. Odlyzko and J. A. Rush "[http://www.springerlink.com/content/l481484244n16157/ On the packing densities of superballs and other bodies]" Inventiones Mathematicae Volume 105, Number 1 (1991), 613-639, [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF01232282 doi: 10.1007/BF01232282] |
* Y. Jiao, F.H. Stillinger, S. Torquato "[http://pre.aps.org/abstract/PRE/v79/i4/e041309 Optimal packings of superballs]" ''Physical Review E'' '''2009''', 79, 041309, [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.79.041309 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.79.041309] | * Y. Jiao, F.H. Stillinger, S. Torquato "[http://pre.aps.org/abstract/PRE/v79/i4/e041309 Optimal packings of superballs]" ''Physical Review E'' '''2009''', 79, 041309, [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.79.041309 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.79.041309] | ||
| + | |||
====Application to nanoscience==== | ====Application to nanoscience==== | ||
* Yugang Zhang, Fang Lu, Daniel van der Lelie, Oleg Gang "[http://prl.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v107/i13/e135701 Continuous Phase Transformation in Nanocube Assemblies]" ''Physical Review Letters'' '''2011''', 107, 135701 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.135701 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.135701] | * Yugang Zhang, Fang Lu, Daniel van der Lelie, Oleg Gang "[http://prl.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v107/i13/e135701 Continuous Phase Transformation in Nanocube Assemblies]" ''Physical Review Letters'' '''2011''', 107, 135701 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.135701 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.135701] | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 14 June 2014
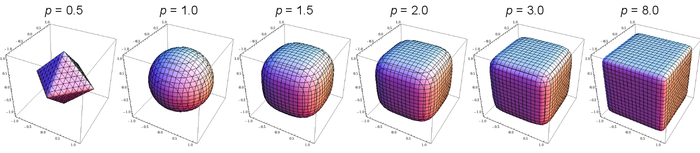
A superball is a general mathematical shape that can be used to describe rounded cubes. In fact, it is a general parametrization that can describe, via a parameter :
- Empty space ()
- Concave octahedra ()
- Octahedra ()
- Convex octahedra ()
- Spheres ()
- Rounded cubes ()
- Cubes ()
The general equation is parametrized by the size, , and the curvature :
Obviously for , we recover the equation for a sphere. In the limit of large , we obtain a cube.
Contents
Volume
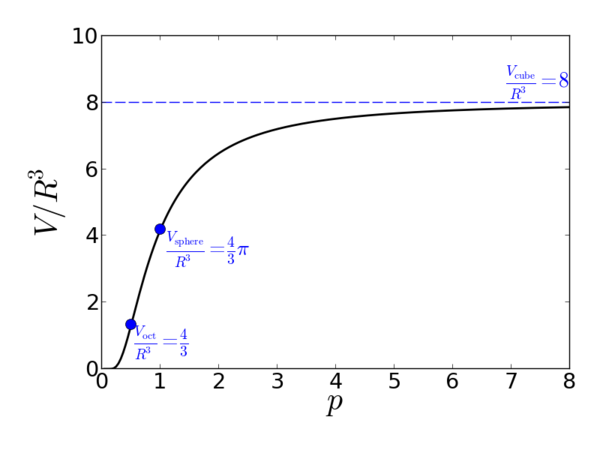
The normalized volume for a superball is:
Where and is the usual Euler gamma function.
Equations
The form factor for a superball is likely not analytic. However, it can be computed numerically.
References
Mathematical descriptions of superballs
- N. D. Elkies, A. M. Odlyzko and J. A. Rush "On the packing densities of superballs and other bodies" Inventiones Mathematicae Volume 105, Number 1 (1991), 613-639, doi: 10.1007/BF01232282
- Y. Jiao, F.H. Stillinger, S. Torquato "Optimal packings of superballs" Physical Review E 2009, 79, 041309, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.79.041309
Application to nanoscience
- Yugang Zhang, Fang Lu, Daniel van der Lelie, Oleg Gang "Continuous Phase Transformation in Nanocube Assemblies" Physical Review Letters 2011, 107, 135701 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.135701