Refraction distortion
Revision as of 13:11, 4 November 2015 by KevinYager (talk | contribs)
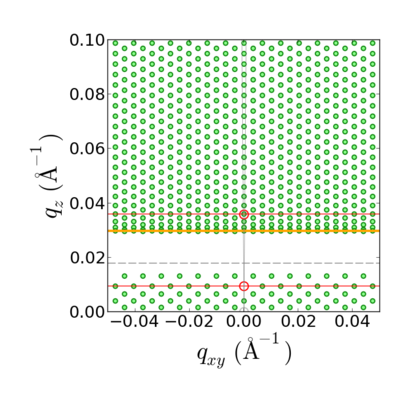
Illustration of GISAXS refraction distortion. The reciprocal-space scattering is a hexagonal array of peaks. However, these peaks are both shifted, and compressed/stretched along qz, due to refraction. This effect is especially pronounced near the Yoneda (orange line).
In GISAXS, GIWAXS, and other grazing-incidence techniques, the refractive index difference between the film and the ambient causes the incident and scattered x-ray beams to be refracted. This extent of refraction depends on the incident and exit angles. Thus, the data that appears on an area detector in a grazing-incidence experiment is non-linearly distorted. This makes data interpretation more problematic.
Refraction Correction
The GISAXS refraction distortion shifts the data along , leaving unaffected.
- Byeongdu Lee, Insun Park, Jinhwan Yoon, Soojin Park, Jehan Kim, Kwang-Woo Kim, Taihyun Chang, and Moonhor Ree Structural Analysis of Block Copolymer Thin Films with Grazing Incidence Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Macromolecules 2005, 38 (10), 4311-4323. doi: 10.1021/ma047562d
- P. Busch, M. Rauscher, D.-M. Smilgies, D. Posselt and C. M. Papadakis Grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering from thin polymer films with lamellar structures - the scattering cross section in the distorted-wave Born approximation J. Appl. Cryst. 2006, 39, 433-442. doi: 10.1107/S0021889806012337
- Rémi Lazzari, Frédéric Leroy, and Gilles Renaud Grazing-incidence small-angle x-ray scattering from dense packing of islands on surfaces: Development of distorted wave Born approximation and correlation between particle sizes and spacing Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 125411. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.125411
- D. W. Breiby, O. Bunk, J. W. Andreasen, H. T. Lemke and M. M. Nielsen Simulating X-ray diffraction of textured films J. Appl. Cryst. 2008, 41, 262-271. doi: 10.1107/S0021889808001064
- Lu, X.; Yager, K.G.; Johnston, D.; Black, C.T.; Ocko, B.M. Grazing-incidence transmission X-ray scattering: surface scattering in the Born approximation Journal of Applied Crystallography 2013, 46, 165–172. doi: 10.1107/S0021889812047887
See Also
- DWBA
- Simulating X-ray diffraction of textured films D. W. Breiby, O. Bunk, J. W. Andreasen, H. T. Lemke and M. M. Nielsen J. Appl. Cryst. 2008, 41, 262-271. doi: 10.1107/S0021889808001064
- Indexation scheme for oriented molecular thin films studied with grazing-incidence reciprocal-space mapping D.-M. Smilgies and D. R. Blasini J. Appl. Cryst. 2007, 40, 716-718. doi: 10.1107/S0021889807023382
- Grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering from thin polymer films with lamellar structures - the scattering cross section in the distorted-wave Born approximation P. Busch, M. Rauscher, D.-M. Smilgies, D. Posselt and C. M. Papadakis J. Appl. Cryst. 2006, 39, 433-442. doi: 10.1107/S0021889806012337

